PSPP Graduate Student Policies and Procedures
This document should familiarize new graduate students with policies and procedures of the Department of Plant Sciences and Plant Pathology (PSPP) and of The Graduate School at Montana State University. The guidelines presented here are sometimes flexible and amenable to modification. The graduate student and primarily the graduate student’s major professor (graduate advisor) and secondarily the student’s graduate or thesis committee ultimately implement these guidelines to create a productive academic experience for the student.
The Graduate School website http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/ includes frequently asked questions, Graduate School forms, dates & deadlines, information for new students, current tuition & fees, policies and procedures (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/index.html), and additional resources. The PSPP website for graduate students is https://plantsciences.montana.edu/studentinfo/grad/index.html. PSPP guidelines align with those of The Graduate School.
Prospective graduate students should communicate with a prospective major professor. This allows the student’s application to be evaluated promptly for entry criteria (e.g., letters of recommendation, etc.). This also enables the new graduate student to identify a research problem at the start of graduate school.
A requirement of the PSPP Department’s graduate program is that students must serve as a Graduate Teaching Assistant (GTA) for at least one semester during their graduate program. When not working as a GTA, you will be working on a Graduate Research Assistantship (GRA). There may be some semesters during which these appointments are combined. These assistantships are offered with the understanding that you are working towards the completion of your graduate degree and making satisfactory progress towards your degree. The 19 hours/week required for these assistantships (GTA and GRA) do not include the time required for the academic and research work necessary to make satisfactory progress towards your degree.
Graduate (thesis) committee
A new PSPP graduate student needs to discuss with their thesis advisor soon after arrival an outline a Program of Study (see Program of Study on The Graduate School webpage http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html). The Program of Study lists what coursework might be needed in addition to the composition of the thesis committee. The thesis committee is formed by mutual consent of the student, the student’s thesis advisor, and prospective committee members. The new graduate student develops a tentative committee list in consultation with the major professor. Once agreed upon, the student contacts prospective committee members to determine their willingness to serve. The thesis committee should be established at least by the end of the second semester, if not first semester. The graduate student files a Program of Study, which lists the members of the graduate committee through MyInfo (after logging in, use the Graduate Committee Requestlink under the Student Services tab).
Once a graduate or thesis committee is formally established, the student should request a meeting of the committee to discuss the proposed thesis research, courses to be taken at MSU, and any other items of concern. The makeup of the graduate committee and proposed course work can be changed with the approval of the major professor and committee and by filing a Program Change form, which is available from http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html.
The composition of the graduate committee is as follows. For master's degree students, a minimum of three committee members is required. PSPP faculty, adjunct faculty, faculty affiliates, faculty from other departments and institutions, and non-academic experts may serve as members. Only PSPP faculty can chair a committee. Off campus and non-faculty appointees must submit a curriculum vitae to The Graduate School for approval (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_masters.html#degreq_masters_committee). Regardless of the exact composition, all members of the graduate committee must be expert in the area relevant to the student's project. For PhD students, departments have the choice of appointing either four or five committee members. At least three members must be within a student's major. At least one, but not more than two, must represent the student's supporting area or minor, if applicable. Adjunct faculty, faculty affiliates, faculty of other institutions, and non-academic experts may serve as members but not as the committee chair. Off campus and non-faculty appointees must submit a curriculum vitae to The Graduate School for approval (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_doctoral.html#doc_committee).
Research focus
The selection of a research topic should be done in consultation initially with the major professor and later with the graduate committee. Identifying a research focus should be done as soon as possible after beginning graduate school, if not beforehand. Once the graduate committee is formed, the graduate student submits a written thesis research outline for feedback to the graduate committee. Students typically present their proposed research as part of the PSPP seminar series during their second semester. This initial seminar focuses more on the aims and background of the proposed research than on the results.
Proposed coursework
Prospective PSPP graduate students are expected to have a strong background and understanding of the biological sciences. This includes an undergraduate degree in one of the many disciplines of biology.
Plant Sciences graduate degree programs have no specific required courses and the student’s graduate committee sets course requirements. PSPP graduate students are required to participate regularly in the PSPP seminar series each semester, which includes presenting a research seminar once a year while enrolled in graduate school. PSPP 594 Graduate Seminar (1 credit) is offered every Fall and Spring semester and graduate students are strongly encouraged, but not required, to enroll in this seminar course, in addition to seminar participation and presentation. Another strongly encouraged course is PSPP 501 Navigating Graduate Studies, which is offer every Fall semester of odd-numbered years.
Course work taken during graduate school should be designed to make up for deficient areas of knowledge, which is determined by the student and the student’s major professor and graduate committee. Ultimately, the graduate student and the student’s major professor and graduate committee determine the specific combination of required formal course work credits and PSPP 590 credits designated as Master’s Thesis (Master’s research) or PSPP 690 credits designated as Doctoral Thesis (Doctoral research). General degree requirements (e.g., the number 400-level credits that can be applied to a Program of Study or the age limit on coursework) are included in The Graduate School website (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_general.html).
By the end of the second semester in graduate school, the graduate student will submit the Program of Study and Committee form (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html) to The Graduate School. This form identifies courses to be taken as part of the student’s graduate school education. PSPP graduate students are responsible for obtaining the signatures of each of the committee members listed on this form. This completed form involves a one-time filing fee of $50 (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/fees_holds.html).
The Graduate School and PSPP Department require a minimum of thirty (30) credits for a master's degree, both thesis and non-thesis (Plan A, Plan B, Plan C). For a master’s degree with a thesis, PSPP combines the required comprehensive examination and thesis defense such that they can be offered simultaneously. Also for a thesis master’s degree, only ten (10) PSPP 590 credits count toward degree requirements along with a minimum of twenty (20) content coursework credits, that latter of which could include research related independent study, seminar, and internship courses (e.g., PSPP 589, PSPP 592, PSPP 594, and PSPP 598). For master’s degree requirements, visit http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_masters.html. For a list of courses that are not allowed to be applied to a Program of Study form, see http://catalog.montana.edu/graduate/policiestext-degree-requirements/#courses_not_approved.
The Graduate School and PSPP Department require a minimum of sixty (60) credits for a PhD degree, of which eighteen (18) to thirty (30) must be thesis credits (e.g., PSPP 690). A maximum of thirty (30) credits from a previously earned master's degree (from MSU or another accredited University) may be applied toward the sixty (60) credit requirement. Doctoral students who have previously earned a master’s degree must take at least twelve (12) formal coursework credits and eighteen (18) to twenty-eight (28) dissertation (690) credits beyond the master’s degree credits. For PhD degree requirements including the details related to comprehensive exams, visit http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_doctoral.html.
|
Suggested MSU courses for PSPP graduate students
(visit Course Descriptions for details of particular courses)
|
Cr.
|
Semester
|
|
AGED 506 – Research Methods
|
3
|
F
|
|
AGSC 401 – Integrated Pest Management
|
3
|
F
|
|
AGSC 441 – Plant Breeding and Genetics
|
3
|
S odd
|
|
AGSC 450 – Plant Disease Control
|
3
|
S odd
|
|
AGSC 454 – Agrostology
|
3
|
S alt
|
|
ARNR 524 – Adv. Animal Breeding
|
3
|
S even
|
|
BCH 524 – Mass Spectrometry
|
3
|
F odd
|
|
BCH 526 – Adv Protein NMR Spectroscopy
|
3
|
F even
|
|
BCH 543 – Proteins
|
3
|
F odd
|
|
BCH 544 – Molecular Biology
|
3
|
F even
|
|
BCH 545 – Advanced Physical Biochemistry
|
3
|
S even
|
|
BIOB 430 – Plant Biotech
|
3
|
S even
|
|
BIOB 476R – Gene Construction
|
3
|
F
|
|
BIOB 477 – Genome Science and Gene Expression
|
5
|
S
|
|
BIOB 484 – Population Genetics
|
3
|
F even
|
|
BIOB 524 – Ethical Practice of Science
|
2
|
S
|
|
BIOM 421 – Concepts of Plant Pathology
|
3
|
S
|
|
BIOM 423/523 – Mycology
|
3
|
F even
|
|
BIOO 433 – Plant Physiology
|
3
|
S
|
|
BIOO 435 – Plant Systematics
|
3
|
F even
|
|
BIOO 437 – Plant Development
|
3
|
S
|
|
BIOO 460 – Plant Metabolism
|
3
|
S odd
|
|
BIOO 465 – Insect Identification
|
4
|
S odd
|
|
CSCI 550 – Data Mining
|
3
|
F even
|
|
CSCI 591 – Special Topics in Bioinformatics
|
3
|
S
|
|
ENTO 510 – Insect Ecology
|
3
|
S alt
|
|
ENTO 516 – Biosystematics
|
3
|
F
|
|
ENTO 520 – Insect Physiology
|
3
|
F even
|
|
ENTO 525 – Insect Morphology
|
2
|
S even
|
|
GPHY 426 – Remote Sensing
|
3
|
S
|
|
LRES 501 – Writing & Professional Develop. for Environ. Scientists.
|
2
|
F, S
|
|
LRES 511 – Environmental Data Mgmt.
|
2
|
S alt
|
|
LRES 525 – Applied Remote Sensing
|
3
|
S
|
|
LRES 529 – Sustainable Cropping Systems
|
3
|
S
|
|
LRES 534 – Environmental Data Analysis
|
3
|
S
|
|
LRES 535 – Tech Of Spatial Analysis
|
3
|
F alt
|
|
LRES 536 – Ecology of Invasive Plants II
|
3
|
Su
|
|
LRES 561 – Belowground Plant Ecology
|
3
|
S odd
|
|
LRES 565 – Environmental Biophysics
|
3
|
S
|
|
LRES 569 – Ecol. Of Invasive Plants in GYE
|
3
|
Su
|
|
LRES 572 – Frontiers in Remote Sensing
|
1
|
S
|
|
MB 528 – Advanced Genetics
|
3
|
S
|
|
MB 530 – Virology
|
3
|
F
|
|
MB 535 – Genomic Analysis Lab
|
3
|
F
|
|
MB 538 – Cell & Molecular Biol.
|
2
|
Su
|
|
MB 544 – Advanced Bioinformatics
|
4
|
S even
|
|
MBSP 579 – Programming for Life Scientist
|
3
|
S
|
|
MBSP 613 – Scientific Proposal Writing
|
3
|
Su
|
|
PSPP 501 - Navigating Graduate Studies
|
3
|
F odd
|
|
PSPP 516 – Research Design and Analysis
|
3
|
F
|
|
PSPP 524 – Advanced Plant Pathology
|
3
|
F odd
|
|
PSPP 541 – Advanced Plant Genetics
|
3
|
F even
|
|
PSPP 542 – Genetics of Plant Improvement
|
3
|
S odd
|
|
PSPP 546 – Herbicide Physiology
|
3
|
F even
|
|
PSPP 548 – Flower Plants of North Rock Mtn
|
2
|
Su odd
|
|
PSPP 550 – Plant Disease Control
|
4
|
TBD
|
|
PSPP 565 – Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions
|
3
|
S even
|
|
PSPP 590 – Master's Thesis
|
|
F,S,Su
|
|
PSPP 594 – Seminar
|
1
|
F,S
|
|
PSPP 642 – Structural and Functional Genomics
|
3
|
F odd
|
|
PSPP 690 – Doctoral Dissertation
|
|
F,S,Su
|
|
STAT 408 – Stat. Computing and Graphical Analysis
|
3
|
F
|
|
STAT 411 – Methods for Data Analysis I
|
3
|
F
|
|
STAT 412 – Methods for Data Analysis II
|
3
|
S
|
|
STAT 437 – Intro to Appl Multiv. Analysis
|
3
|
S
|
|
STAT 446 – Sampling
|
3
|
F
|
|
STAT 448 – Mixed Effects Models
|
3
|
F
|
|
STAT 502 – Intermediate Mathematical Statistics
|
3
|
S
|
|
STAT 505 – Linear Models
|
3
|
F
|
|
STAT 506 – Advanced Regression Analysis
|
3
|
S
|
|
STAT 511 – Methods of Data Analysis I
|
3
|
F
|
|
STAT 512 – Methods of Data Analysis II
|
3
|
S
|
|
STAT 534 – Spatial Data Analysis
|
3
|
S odd
|
|
STAT 446/536 – Time Series Analysis
|
3
|
F even
|
|
STAT 541 – Experimental Design
|
3
|
S
|
Grades
Graduate students must maintain a GPA of 3.00 for all courses listed on the Program of Study form. Any listed course for which a grade lower than a C- has been received is considered failing (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/grades_academicstanding.html). Two or more courses with failing grades could result in dismissal from the PSPP graduate program.
Teaching
The PSPP department requires that all graduate students have teaching experience during graduate school. This includes teaching at least one biology course offered on the MSU campus, as determined by the student and major professor. To assist with the teaching of a course, a student must receive an invitation from the course instructor.
Departmental exams
Master’s comprehensive exam and defense of thesis
During the final semester of a master’s thesis project, the student will be examined over both research and general knowledge of coursework. Course work thus should be finished preferably well before the final semester. The oral exam and thesis defense usually lasts about 3 hours. Immediately prior to the exam, the student will be expected to present a seminar on the thesis research. Topics covered in the exam are the prerogative of the committee members but are usually related to a general knowledge of plant sciences, topics covered in graduate classes, and any aspect of the thesis research.
PhD comprehensive exam
Typically, the PhD comprehensive exam occurs at the end of the second year, which is generally when formal course work is completed. The comprehensive exam comprises two parts. The first is written and includes a set of questions presented to the major professor by each graduate committee members. The student answers each committee member's set of questions usually within four hours. Within 10 days or so after the written comprehensive exam, the oral comprehensive exam is scheduled. The student may be allowed to see the results of the written exam prior to the oral exam and this is determined by each committee member. The oral exam usually lasts three hours and includes questions from each committee member. Oral questions can follow up those on the written exam or they may cover any other area a committee member chooses. To pass the comprehensive exam the student must perform satisfactorily on both the written and oral portions of the exam. If the student fails the exam, a second opportunity at least six months later may be provided by the graduate committee (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_doctoral.html). For a PhD degree, the PSPP Department provides the option of combining the required comprehensive examination and thesis defense such that they can be offered simultaneously. Taking the comprehensive exams well before the thesis defense is recommended so that the graduate student has certainty of PhD candidacy well before defending the thesis.
PhD final exam and thesis (dissertation) defense.
When a student has completed the thesis research, a final examination will be scheduled. The student is expected to present a seminar covering the thesis research, which occurs commonly immediately prior to the final exam. The PhD final exam usually covers the thesis research, but the student should also be prepared to answer questions covering any material pertaining to the student’s prospective career. If the final exam is failed, it may not be repeated for at least two months (see website immediately above).
Thesis (dissertation) writing and preparation of papers for publication
The Graduate School prescribes thesis or dissertation format and style (https://www.montana.edu/etd/index.html). Any concerns here should be taken up with the staff of The Graduate School. PSPP encourages graduate students to put their thesis research into a broad context by writing a literature review. The following books on scientific writing might provide helpful information prior to thesis writing:
DAY, R.A. 1983. How to write and publish a scientific paper. 2nd Edition. ISI Press, Philadelphia. ISBN 0-89495-002-3.
O'CONNOR, M., & WOODFORD, F.P. 1975. Writing scientific papers in English. Elsevier-North Holland. New York. ISBN 0444-15165-6.
A goal of a student’s thesis research is to have their work nationally recognized and readily available to the scientific community. Students should prepare appropriate portions of their thesis for publication in a peer-reviewed journal. The student's priority is to conduct thesis research and write the thesis while simultaneously preparing manuscripts for publication in a refereed journal. In the end, thesis writing should expedite peer-reviewed journal publication. This could involve the inclusion of manuscripts in preparation, in press, and published as separate thesis chapters.
The Graduate School webpage Electronic Theses and Dissertations has useful tips for preparing and writing theses, in addition to information on theses submissions and submission deadlines.
Seminar preparation and procedures
Each student is required to present at least one seminar per academic year. In the semester the student presents their seminar, they must also register for PSPP 594-01. All students are also required to attend regularly the department seminar series. The purpose of seminar is twofold. It promotes camaraderie among students, staff, and faculty, and the ever-important social face of the scientific enterprise. It also serves to provide the student with the experience of presenting information before a group of peers and colleagues. Such communication experience is invaluable to becoming a public speaker and lecturer, which is crucial for success as a scientist. The student’s major professor must approve the seminar topic. Students are encouraged to use PSPP 594-01, seminar, for presenting their thesis proposal and defense.
In general, structure seminars like a journal article. The introduction should comprise a background and literature review to acquaint the audience with the topic. This should be followed with explanation of the scientific approaches and methods. Results and discussion should be explained in enough detail to be understood by a scientifically literate audience. The seminar should conclude with a general discussion of the implications and applications of the work.
The department provides the facilities, equipment, and expertise such that a graduate student can give an excellent presentation. This includes preparing slides that report information in an aesthetically appropriate manner, managing time limits, and finding an audience with which to practice seminar presentation more than once before the formal presentation. The major professor and possibly the thesis committee members or other PSPP faculty should approve in advance any seminar presented by a graduate student.
Graduating
Before a graduate degree and approval for graduation can completed, each student’s Program of Study must be evaluated to ensure that all requirements have been met. This is an important step for a student and the university as it ensures that proper credit has been given for all student effort. Once approved and complete, the student has full assurance that they have met all the degree requirements and can file for graduation. The Degree Audit Fee ($20) will be a recurring fee each time a student files an Application for Advanced Degree. This fee will be applied directly to your student account. The graduation fee ($30) is a one-time fee incurred at the time a student applies to graduate. This fee will be applied directly to your student account (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/fees_holds.html).
Deadlines and dates
One of the responsibilities of a graduate student is to meet all the dates and deadlines reported by The Graduate School (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/dates-deadlines.html).
Summary: The Graduate Student Roadmap
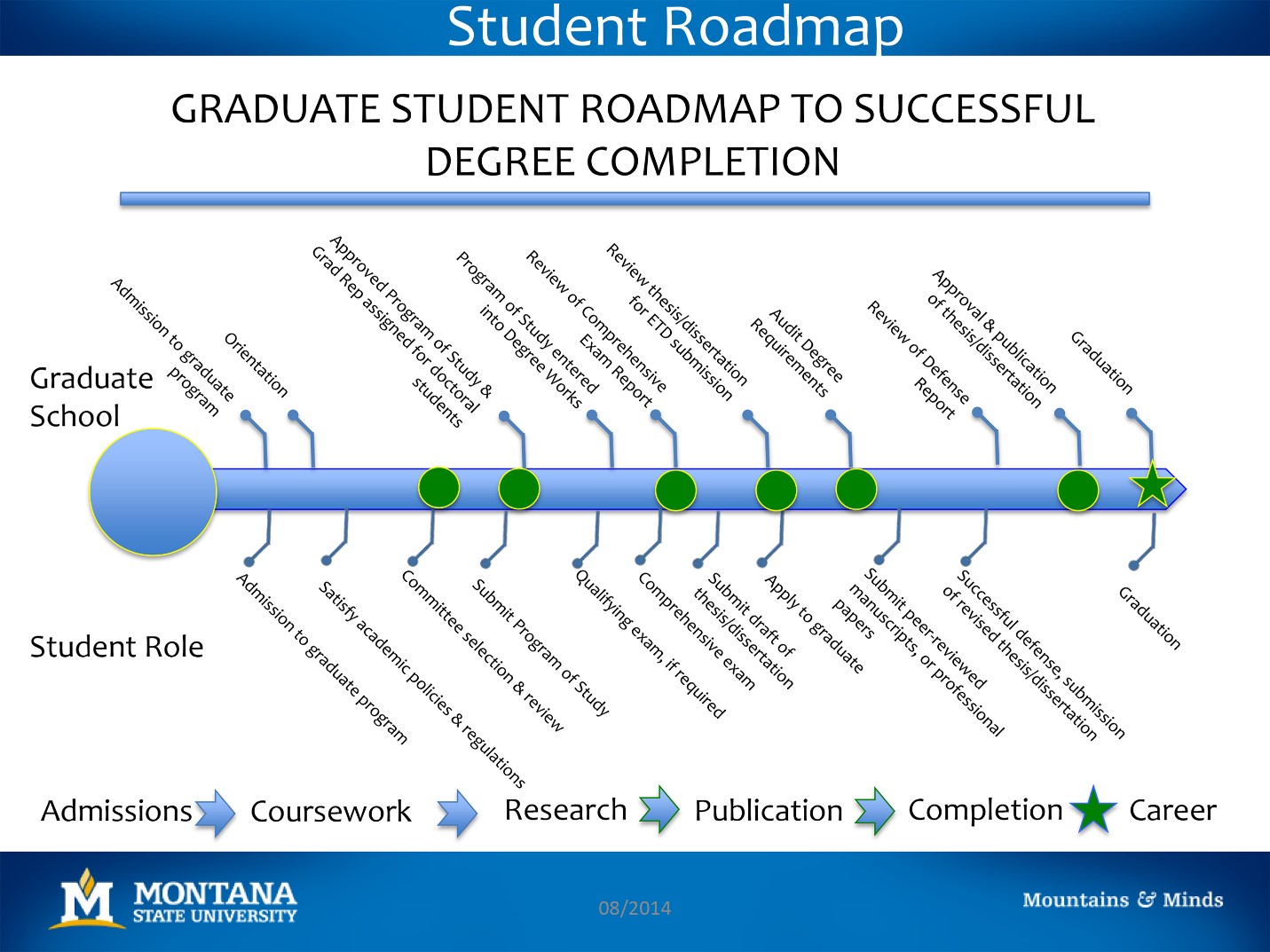
The above graphic is from an orphaned Graduate School webpage but it may provide direction in planning your graduate school agenda (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/resources/coffee_talk/Roadmap.pdf).
Residency requirements
For non-resident domestic graduate students wanting resident status in the state of Montana, see https://www.montana.edu/registrar/residency/index.html. Out-of-state graduate students can expect to pay in-statue tuition if they receive a GTA or GRA while enrolled in the graduate school.
The experiences of PSPP international graduate students suggest that if you are an international student on an F-1 visa, you are unlikely to receive residency status. This is true even if you are paying state taxes, own a Montana driver’s license, and own a house in Montana. Applying for Montana residency for avoiding out-of-state tuition works for graduate students who are U.S. citizens or hold a green card. Regardless, international students on an F-1 visa and with a GTA or GRA appointment will pay in-state tuition. An issue may arise with out-of-state tuition for international students, for example, when registering for a 1-credit extension in the final semester without a GTA or GRA appointment.
Stipends, fellowships, and awards
Graduate Research Assistantships and Fellowships (GRAs) from a variety of sources, or perhaps their own personal funds often support students. Usually this is determined prior to admission to study in the department. In addition to the above, there are several awards available on campus for which students may compete and which can serve to supplement their regular stipend.
E.L. Sharp Graduate Achievement Award –A fund established in honor E.L. Sharp, who
retired from the department in 1987, is to reward the graduate student in Plant Pathology
who makes a significant accomplishment. This can include an outstanding thesis, poster,
or oral presentation at a meeting. Usually the award is presented each year. The faculty
members or students may nominate a student for this award, or a student may apply
for it. A faculty committee determines the winner using the documentation provided
Leonard Chvilicek Award – This award is given to a graduate student who is working
on a problem related to wheat production or improvement. Preference is given to a
Montana high school graduate, and recipient must have an agricultural background (i.e.,
from a farm or agribusiness family). Plant breeding faculty select the recipient annually.
Robert F. Eslick Memorial Award – This award was established in memory of Robert F. Eslick, who had a long and distinguished career as a plant breeder and agronomist at Montana State University. The award is made to a full-time graduate student in crop science who shows academic and professional promise, with preference given to a graduate of a Montana high school. Plant breeding faculty select the recipient annually.
Work expectations supported by graduate research assistantships
The work performed by a graduate student, although contributing to the productivity of the major professor and the department, is nevertheless primarily for the benefit of the student. Research leading to publications is a major criterion by which students are judged for the rest of their career and is a crucial factor in obtaining a desirable job or postdoctoral appointment. A GRA is technically a half-time appointment requiring 20 hours per week spent on research. However, most students find it necessary and desirable to spend significantly more time to maintain a suitable rate of progress towards a degree. Normally, the student determines what rate of research progress is desirable to produce peer-reviewed publications. If needed, sufficient research effort and progress can be decided by the student, major professor, and graduate committee. Reappointment each semester will be contingent upon satisfactory performance in research and coursework, as determined by the major professor and availability of funds.
Vacation and holiday policies and expectations
Graduate students are regular University employees regarding vacations and holidays. Thus, on the days when the University has an officially scheduled holiday and offices are closed, students may also observe such holidays. If there are any questions as to what days are holidays, check in the university calendar http://calendar.msu.montana.edu/academic-term-calendar. In some cases, classes are dismissed but the offices are open. Students should regard such days as regular work days. Students on GRA's are entitled to two weeks of vacation each year but they should consult with their major professor about when that time will be taken. In general, the time intervals between academic semesters and regular work commitments should be viewed as valuable opportunities to spend quality time on research.
Attendance at regional and national meetings
Professional meetings provide the best access to up-to-date information and colleagues working in your research area. In general, we encourage any student attending relevant professional meetings to present a paper or poster since this provides an excellent opportunity to present your work before a group of peers. The major professor, principal investigator, or project leader provides the funds for students attending professional meetings.
Job hunting
Students interested in finding a position should check job announcements in the publications of major science journals, such as Nature or Science, websites such as HighEdJobs (https://www.higheredjobs.com/), or the journals of professional societies such as Agronomy News, Phytopathology News, ASHS Newsletters, American Journal of Botany, and Crop Sciences. For preparing a CV or resume and efficiently searching for jobs, Career Services offers advice at http://www.montana.edu/aycss/careers/planning/index.html.
Membership in professional societies
Most academics and scientists belong to professional societies associated with their area of interest. The purpose is to benefit from the services provided by such societies. This includes publication in professional journals, job placement services, and organizing professional meetings at regional, nation, and international levels. Students are strongly encouraged to become members of relevant scientific society. Most societies have discounted rates for student members (e.g., Crop Science Society of America, https://www.crops.org/; Entomological Society of America, https://www.entsoc.org/).
Departmental office and staff
The staff in the main offices, Leon Johnson Hall 324 and Plant BioScience (PBB) 119, have an open-door policy for students. The PSPP staff can answer most general questions that you might have about the campus and the department. Use of office computers and printers is limited just to the office staff. If you have additional questions, please contact Irene Decker at 994-5171, 119 PBB, decker@montana.edu.
Ordering of lab supplies is coordinated through the major professor or lab manager. Office supplies are ordered through the department staff. Please contact your major professor regarding ordering procedures. Irene decker (decker@montana.edu), 119 PBB, is the administrative staff person knowledgeable about who at MSU should be contacted whether it be a question regarding ordering and billing or a general question related to anything about campus or the department.
Regarding office space for graduate students, seniority determines assignment of student desks. Changes are made when space becomes available or when agreed upon between students. Individual graduate student mailboxes are in 119 PBB or next to the elevators in 324 Leon Johnson Hall, depending on where your lab is located.
The Graduate School staff
The Graduate School main office is 108 Montana Hall. The Graduate School web site http://www.montana.edu/gradschool includes contact information and many other resources for new graduate students, including a list of staff who may be contacted for questions (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/staff.html). All PSPP graduate student guidelines align with those of The Graduate School. While the above Graduate School office staff can be contacted for guidance, the student’s major professor should be consulted first in this regard.
Use of departmental equipment, vehicles, and space
The equipment and facilities owned and occupied by the department are here to be used for research. In many cases, however, specific pieces of equipment have been purchased by grants and/or are assigned to specific faculty members. To use such items, please contact the individual responsible for the item. Not only is it a common courtesy, but it will allow the best scheduling of and the proper use of the equipment. The various PSPP labs stock many chemical and other disposable items. Borrowing such supplies is typically possible if permission of the lab director is sought prior to borrowing.
Space for students in the Plant Growth Center (PGC) is requested via the student’s major professor. Space in the PGC is under the control of the PGC Advisory Committee, headed by David Baumbauer, Manager of the PGC. To obtain permission to use such space, an application form must be filled out by the major professor and filed with David Baumbauer (contact information listed at http://plantsciences.montana.edu/directory/staff/index.html).
Research space on the Post Research Farm, the Ft. Ellis Research Plots, and on the Horticulture Farm is under the control of various committees. The student’s major professor should be consulted about the procedures for obtaining use of such space. Usually there is a meeting of the various Farm Committees in the spring prior to the planting to determine space needs for the coming growing season, including space for fall-seeded crops. If a student uses space on any of the Research Farms, they are expected to maintain it in a weed-free condition.
Frequently asked questions
The Graduate School also posts frequently asked questions (see http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/faq.html).
1. Can students transfer courses taken at another university to MSU?
Yes. Thirty credits from a completed master’s degree can be applied to the sixty required for a PhD degree. Otherwise, the number of semester hours transferred from other institutions (non-degree or degree status) combined with credit(s) taken as a non-degree graduate at MSU may not exceed nine (9) credit hours (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_general.html).
2. Before taking a semester off, what do students need to do?
A continuous enrollment policy (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/enrollment.html) of MSU requires students wishing to take time away from their programs to inform their major professor (graduate advisor) and department of their plans. The six- and ten-year limits for completing master's and Doctoral degrees are calculated from the start of their programs. Time away from a program is not considered a reason for these time limits. Returning students need to submit an Intent to Register form (http://www.montana.edu/registrar/Returning.html).
3. What is difference between master’s "A" and "B" Plans?
See the website http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/degreq_masters.html.
4. What is required or what can be included in a program of study?
The Program of Study allows graduate students to customize their advanced degree (see program of study form linked from https://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html). Once approved, this document becomes a contract with The Graduate School and graduate student that defines the work that must completed before a degree is received. Programs may be revised and updated to reflect the availability of classes and shifts in academic foci (see revision of program forms linked from https://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html).
5. During pursuit of a master’s degree, can I switch to a PhD program of study?
File the change of graduate status form (linked from https://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html). The PhD committee is then formed by filling out a new program of study form (see link on website: https://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html). The policy of The Graduate School is to NOT allow Master’s Thesis credits (590 credits) to transfer to Doctoral Thesis credits (690 credits) when a student switches from a Master’s program to a PhD program.
6. When do students need to submit a Graduate Program of Study and Committee Form?
This must be submitted to the Graduate School by the end of the second term of study for master’s students and by the third semester for PhD students. Failure to do so will result in the student being placed on academic probation for failing to make satisfactory progress toward a degree (see relevant form linked from https://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html).
7. Can students change their committees if they have trouble scheduling their comprehensive exams or defenses to include all members?
Students should schedule all committee meetings as far in advance as is practical to coordinate all members' schedules in time to satisfy all deadlines.
8. How can students change their programs of study?
A student must submit the changes on a Change of Program form with the signatures of the major professor and department head. Completed courses may not be removed and students must repeat any course in a program where a grade below a C- was earned. The relevant form can be found at https://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html.
9. How can students change their graduate committees?
Students must submit a "Graduate Committee Revision" form with the changes, reasons, and signatures of the faculty being added or removed (the relevant form is linked from https://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html).
10. What are the formatting requirements for theses and dissertations?
The requirements for formatting theses and dissertations are found on The Graduate School website http://www.montana.edu/etd/. These guidelines supersede departmental and discipline standards and must be followed if students wish to have their work accepted by The Graduate School. Although it is the students' responsibility to see that their theses or dissertations conform to The Graduate School requirements, the major professor should ensure that students do not submit work with significant formatting errors. Please be aware of the specific deadlines for submitting a thesis or dissertation each semester.
11. How do students set up their comprehensive exams or defenses?
While coordinating with the major professor, the graduate student schedules a comprehensive exam or defense so that all members can be present. The time and location of the public presentation portion of the thesis defense should be announced within the department at least two weeks in advance. Please email Irene Decker at decker@montana.edu with the details of the thesis defense. A flier will be created and sent for approval by the student before being distributed. Students must be registered for at least three credits in the semester in which the thesis defense occurs. The Graduate School deadline to complete all requirements including approval of thesis precedes the last day of the semester (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/dates-deadlines.html).
12. How does a student arrange to graduate?
Complete all degree requirements by the end of the final semester, during which register for at least three credits and file a Graduation Application with The Graduate School (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/forms.html#forms_graduation) by September 20 for Fall Semester, February 5 for Spring Semester and June 10 for Summer Semester (http://www.montana.edu/gradschool/policy/dates-deadlines.html). Failure to meet these deadlines requires registering for three credits and graduating the following semester.
